
Aluminum is a lightweight metal, with a silvery-white appearance.
This article is centred on simplifying the complexity of aluminum welding for both beginners and experts. It explores everything you would like to know about welding aluminum.
Whether you want to learn how to prepare aluminum, welding technique or precautions – this guide will make you an aluminum welding expert.
What Makes Welding Aluminum Difficult?
Although you can weld aluminum, there are certain challenges you will deal with such as:
Oxide Layer:
Aluminum has an outside oxide covering which has a higher melting point than the metal. As such, it is a prerequisite to first remove the oxide layer before welding the base metal.
Limited Workability Window:
Aluminium’s high affinity to hydrogen gives you a limited time to weld it.
The more it heats up, the more it absorbs hydrogen. When it aluminum absorbs more hydrogen, it becomes porous and weak metal.
Impurities:
At times, aluminum may have impurities. These impurities will interfere with the aluminum welding capability.
Examples of such impurities include dirt, air, and water. These impurities can fuse into the metal during welding.
Workability Complexity:
Welding aluminum will require you to use aluminum of varying thicknesses. This can pose an uphill task for you.
Apart from the above, aluminum also:
- Has a Low melting point – making it prone to burnout during welding.
- Does not change colour before reaching its melting point. Consequently, you may end up overheating the aluminum during the welding process.

Indeed, welding aluminum comes with its challenges. However, these shortcomings are not enough to make you shy off.
By using this guide and constantly practicing, we trust you can be able to weld aluminum without any difficulties.
How to Weld Aluminum Successfully
In the previous section, we looked at why welding aluminum can be challenging. This section gives you a general guideline to enable you obtain a successful aluminum weld.
Below are steps to help you prepare your aluminum before welding:
Step 1: Removing Impurities
First, remove impurities such as oil, grease, or water vapor from the aluminum surface.
You can use either a solvent or a moderately alkaline solution such as acetone or strong soap.
Step 2: Eliminate Any Oxide Layers
Next, you need to rid aluminum of any oxides.
Unlike in the removal of impurities, in this stage, you can use acid or a strongly alkaline solution. Alternatively (and preferably) you can employ a stainless-steel wire brush.
After this, you can proceed to weld aluminum.
However, if you plan to weld aluminum later, you can:
- Cover the intended joint to prevent any contamination after cleaning
- Store the aluminum under dry and room temperature conditions.
Note: Ensure you promptly weld the aluminum. Storing the aluminum for an extended period will require you to redo the cleaning process.
Best Techniques for Aluminum Welding Successfully
This section covers the main aluminum welding techniques.
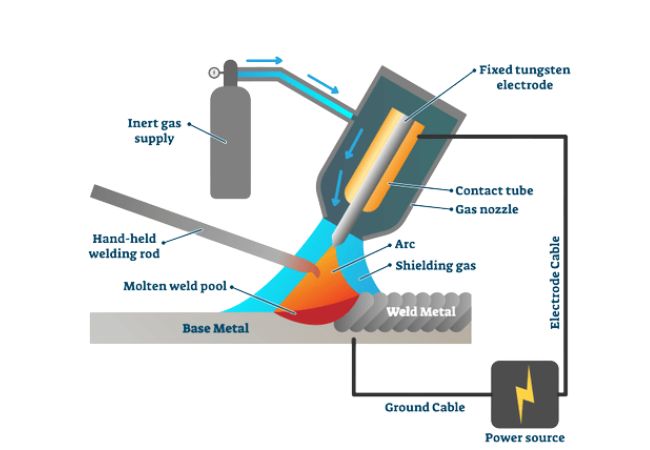
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) Aluminum
Tungsten Inert Gas or CTAW is a common technique when it comes to welding aluminum material.
TIG depends on a gas to protect the welded aluminum section from any possible contamination.
The main shielding gas is argon.
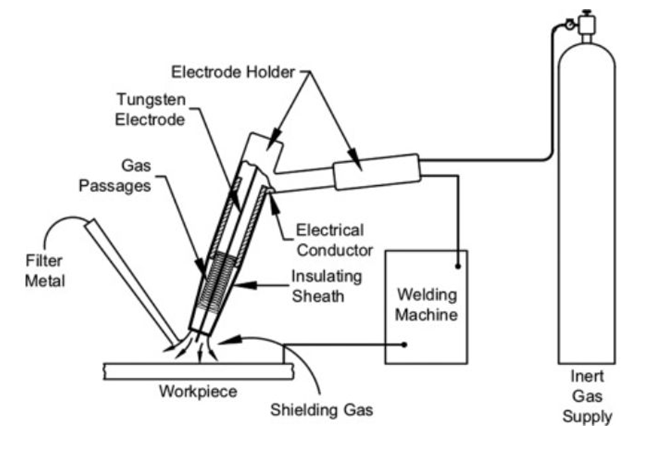
Equipment:
Equipment for TIG welding should have the below:
- Constant current
- Alternating current (AC) capability
- Use 100 percent Argon as the shielding gas
Application:
There are many industries using this welding technique such as:
- Automotive industry by professional race team welders.
- Food and pharmaceutical industry for welding food or medicine containers.
Process:
GTAW involves feeding the filler material through a paddle. You will follow these key processes:
- First, select an appropriate filler material. Commonly, tungsten rods are the preferred choice.
- After the first step, clean and preheat the aluminum
- Ensure you can regulate the argon flow at the torch. Unregulated carbon can result to an irregular arc. Most GTAW equipment have a peddle mechanism to help in the regulation.
- For the elimination of any warping incidences, you can use a heat sink.
- Ensure that the filler is contaminant free.
- Finally, melt the aluminum using your equipment to create a paddle.
Advantages:
- It uses alternating current which cleans off the oxidized layer during welding.
- Gas shield prevents any contamination of the aluminum during the welding process.
- Produces stronger and more ductile welds.
- Suitable for thin aluminum pieces.
- Ideal for DIY projects
Disadvantages:
- Require manual feeding of the filler material to the paddle. This requires extra accuracy.
- It’s slower compared to other welding techniques.
- Requires regular regulation of the shielding gas to prevent build-up.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Aluminum
GMAW is the same as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding.
This method also incorporates the use of argon as a shielding gas during the welding process.
However, in GMAW the wire is fed mechanically and not manually as in GTAW.
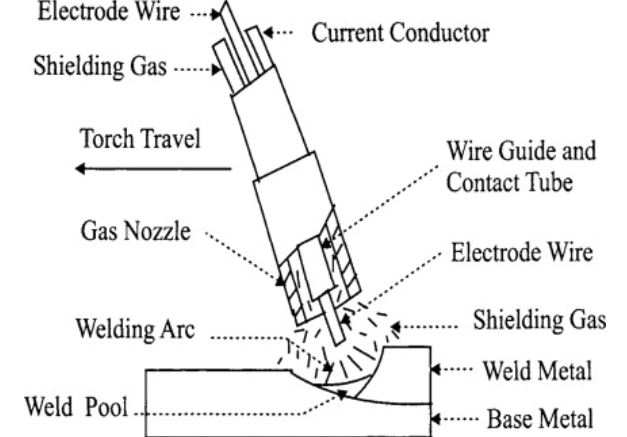
Equipment
You will require a spool gun or push gun. Either of these will aid in the mechanical feeding of the wire.
You should connect the aluminum welding machine to constant voltage and current.
Application:
Some industries that depend on this technique are:
- Automotive
- Construction
- Manufacturing
Process:
GMAW is described as a ‘hot and fast’ process. As such, ensure you have the below in place before initiating the welding.
- Select a filler material with the same melting point as your base material.
- Prepare either your push gun or spool gun
- Clean the aluminum to remove any oxides.
- File the edges which you intend to join
Once all the above are in place, you can proceed to do the weld.
During welding ensure the below:
- Use argon as the shielding gas. Argon has a good penetration profile and cleaning action.
- Employ the push technique. Push the gun away from the weld puddle. This will increase shielding gas coverage, reduce weld contamination, and increase cleansing.
Remember, the process should be ‘hot and fast.’
Advantages:
- MIG welding has a high deposition rate.
- Easy to learn how to use and control the MIG equipment
- It uses a shielding gas that helps prevent contamination.
- One-hand operation increases welding speed.
- Ideal for DIY projects.
Disadvantages:
- High risk of potential burn-through of the base material if you are not careful.
- The equipment is limited to indoor use.
- The spool or push guns have a relatively high upfront cost.
- Not suitable for thin aluminum pieces
Aluminum Arc Welding
Arc welding is the first-ever welding technique. Stick welding and arc welding are the same thing.
In arc welding, the power will help in melting and welding metal sheets together.
Despite the widespread use of arc welding, a significant level of expertise is required to achieve a successful aluminum arc weld.
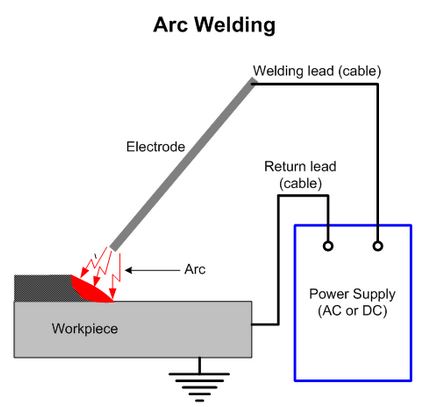
Equipment:
Arc welding uses a specialized machine referred to as an arc welder. You can adjust the heat generated by the machine depending on the metal you are welding.
Application:
If you are an expert, you can use arc welding to weld aluminum metals in all industries.
It is ideal for larger projects.
Process:
- First, prepare your outdoor welding workspace. For indoor arc welding, ensure the room is well-ventilated and has no combustible items.
- Like MIG and TIG, you will need to clean the base aluminum and rid it of any oxides.
- Next, you will preheat the aluminum to about 4000
- You must ensure that the arc welder is at low amperage to avoid any burnout or distortion.
- Striking an arc carefully and consistently on the base aluminum metal is the second last step.
- Finally, you will carry out the post-weld clean up. This involves first submerging the welded aluminum in water. Subsequently, proceed to chip off the slags then wipe the base metals with a piece of dry cloth.
Note: When conducting arc welding, protective gears are a must:
- Helmet – For shielding your eyes
- Gloves – For protecting your hands since you have to hold the electrodes.
Advantages:
- Unlike MIG and TIG welding, arc welding is ideal for outdoor conditions.
- Also, arc welding is cost-effective.
- Produces robust and lasting weld
Disadvantages:
- Compared to MIG and TIG welding, arc welding is complex and requires a high level of expertise.
- Uses coated electrodes instead of shielding gas. This results to flax formation.
- Requires post-weld clean-up which is tedious.
Aluminum Electron Beam Welding
Electron Beam (EB) welding depends on the kinetic energy of electrons to heat the part before transferring the heat.
Notably, EB welding is conducted in a vacuum chamber. It is ideal for 6000 series aluminum.
EB welding has a high speed of up to 100 inches per minute (ten times the speed of TIG and MIG welding).

Equipment:
There are specialized EB welding machines. These machines can be standardized and customized depending on the intended use.
Application:
Aluminum EB welding is done in most industries including:
- Aerospace Industry
- Medical Industry
- Energy Industry
- High-tech Industries
Process:
- First, you will need to clean your aluminum base metals to remove any oxides and hydrocarbons.
- Since EB welding is a fusion welding technique, you will not require any filler material.
- Ensure you conduct the welding in a vacuum environment.
- During welding, be precise with the joint. It’s at the joint where the heat is generated, and the fusion occurs.
Advantages:
- High accuracy and precision in the weld.
- EB welding features not less than 97% strength retention.
- Since EB welding is done in a vacuum chamber, it results to a clean weld.
- There is a possibility of full automation of the EB welding process.
Disadvantages:
- It is complex to set up and start-up EB welding due to the vacuum chamber.
- The complexity makes EB welding less cost-effective.
Laser Beam Welding Aluminum
Laser Beam (LB) welding is a non-contact, vacuum-less welding option. It uses laser beams to create a weld.
With LB welding, you can attain a fast welding rate of up to 200 inches per minute. Additionally, the accuracy levels are also impressive.
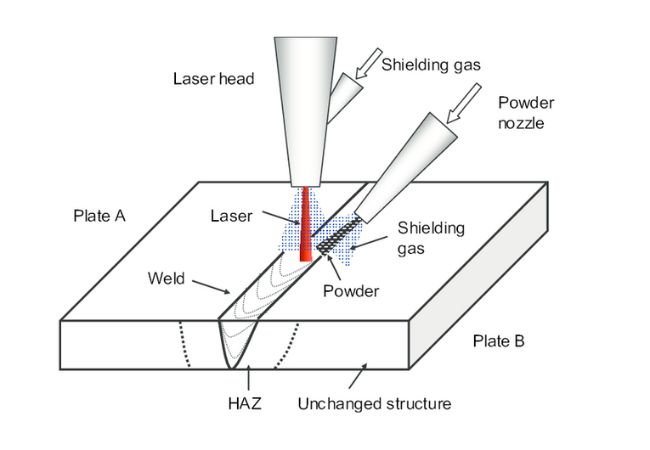
Equipment:
There are various laser welding equipment. The two main laser machines are:
- Manual Lasers
- Computer controlled lasers
The various machines have different controls and beams.
Application:
Laser welding for aluminum is used in instances where a high welding rate is required.
These applications can range from the aerospace industry to the medical field.
Process:
i. Laser welding is conducted by professionals. However, below is the basic guide for laser welding:
ii. First, you will need to clean the aluminum metals before welding.
iii. Next, ensure the joints are also clean and ready for welding.
iv. You can then proceed to weld. Depending on the technology of the machine, the laser beam can either be:
- Pulsed laser – Beam is switched on and off at extremely high rates of about 10-1000hz
- Continuous laser – Characterised by a steady beam of laser, it is ideal for deep penetration welds.
- Laser Stir – Continuous beam of laser swings at a very high rate causing a stirring action.
Advantages:
- Fewer defects on the aluminum welds.
- High precision during welding.
- Easy set since it doesn’t require a vacuum chamber.
- It uses shielding gases which enables you to attain a clean weld.
- Cost-effective due to high welding rates.
Disadvantages:
- Can only be done by experts.
- The initial cost of the laser machines is relatively high
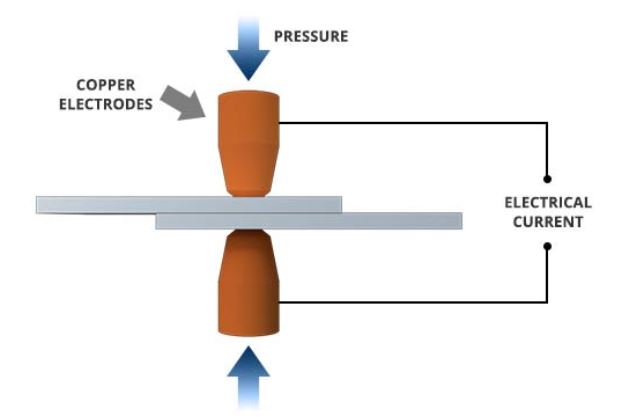
Aluminum Spot Welding
Spot welding melts two pieces of metal to form a weld.
It uses a pair of electrodes for two main purposes:
- Clamping the base metals
- Delivering the base metal needed to make the weld.
Simply put, spot welding joins the aluminum metals together with heat from an electric current.
Equipment:
The equipment used is a spot welding machine.
Importantly, you should have a three-phase electrical power system.
Also, spot welding requires an extremely high current of about 150 amps per phase.
To counter this, you can use a capacitor discharge welder which significantly reduces the power draw during welding.
Application:
Aluminum spot welding is carried out in most industries, especially the automobile industry.
Process:
- As in other welding techniques, ensure you first clean the aluminum metals.
- Wear the necessary protective gear.
- Ensure that your power supply can support your spot welding equipment. A sign that your power supply is not sufficient will be the flickering of lights on your premise.
- Proceed to weld the base metals quickly.
- Finally, water-cool the electrodes due to short weld times coupled with high current.
Advantages:
- Quick and efficient.
- Does not require filler or fluxes.
- Special skill is not a prerequisite
- You can automate the spot welding process
Disadvantages:
- Can only efficiently weld aluminum of thickness ranging between 5 to 50 inches
- The size and shape of the weld are directly proportional to the size and shape of the electrodes.
- There is a high probability of joint warping.
Advantages of Aluminum Welded Parts
Aluminum has replaced steel in several applications where weight is crucial.
The advantages of aluminum welded parts stem from the properties of aluminum. Below, are the key benefits of aluminum welded parts:
- Durability – When exposed to air, the aluminum welded parts will form an oxide layer. This layer will protect the part from corrosion.
- Quick welding – Since aluminum has good thermal conductivity, its faster to weld compared to other metals such as steel. Consequently, aluminum welded parts are quick to deliver.
- Strength alteration – Although aluminum welded parts are not stronger than their steel counterparts, they can be treated to match the strength levels of steel.
- Easy machinability – Aluminum welded parts are easy to cut hence working with them is not that difficult.
- Aesthetic value – Provided you weld the correctly, aluminum welded parts are usually appealing to the eye.
- Lightweight – Finally, aluminum welded parts are relatively light hence are easy to transport and work with.
Aluminum Welding Tips and Tricks
As earlier mentioned, welding aluminum is not a walk in the park. However, the purpose of this entire article is to help you navigate the aluminum welding world with ease and comfort.
The below tips and trick will aid you in successfully welding aluminum:
- Take safety measures – Safety first! Ensure you put on a PPE kit during welding to ensure your safety. These include safety gloves, goggles, welding helmets, and protective shoes. This applies both to the skilled and the newbies.
- Be detailed-oriented – Aluminum is a sensitive metal. As such, you need to be very attentive during welding.
- Proper preparation – As highlighted throughout this article, preparation is vital in aluminum welding. First, you need to clean and protectively store the aluminum you intend to well. Also, prepare yourself with the best technique to efficiently weld the pieces.
- Proper cleaning – To clean aluminum, first use a solvent like acetone to remove deposits such as oil, droplets, and grease on the surface. Next, you can use a strong alkaline, moderate acid, or steel brush to get rid of the oxide layer.
- Patience – Welding in a hurry is not only dangerous but will also result in poor welds. Sequentially follow the various welding steps.
How to Choose Best Filler Material for Aluminum Welding
Most aluminum welding techniques will require you to use a filler material. Undoubtedly, your choice of filler material will affect the quality of the final well.
Below are some key considerations you should make when selecting a filler material:
- Welding equipment – The amperage and the properties of the welding equipment should be able to accommodate the filler material you choose.
- Welding condition – Your chosen filler material should be compatible with shielding gas. Alternatively, it should be also compatible with the welding condition such as a vacuum surrounding.
- Regulatory specifications and codes – Ensure you go for a filler material that is at par with the industrial standards of aluminum welding.
- Base material – In our case, the base material is aluminum. Choose a filler material that is compatible with aluminum.
Aluminum Alloys Suitable for Welding
The table below has a summary to guide the selection of suitable aluminum for welding.
We have divided it into three main sections:
- Suitable for Welding – We highly recommend aluminum under this section for welding.
- Can be used but is not optimum – You can use aluminum alloys under this section for welding. However, they are not the most desirable.
- Experience-based Welding – Welding these alloys are highly tied to high experience levels due to their complexity.
| Series | Alloy | Common applications | Composition | Key Property |
| Suitable For Welding | ||||
| 5000 | 5052 | Pressure vessels, marine applications, hydraulic tubings | High levels of magnesium. | Ideal for high-strength material used in heavy-duty application |
| 5083 | Marine components and cryogenic applications | |||
| 5454 | High Heat applications | |||
| 6000 | 6061 | Automotive, aerospace, pipeline | Alloys comprise magnesium and silicon | Useful in welds found in buildings and structures |
| 6063 | Medical equipment, extruded parts | |||
| Can be Used But is Not Optimal | ||||
| 1000 | Applications aimed at withstanding chemicals | Almost 99% aluminum | Useful in applications that require less strength but more resistance to corrosion | |
| 3000 | 3003 | Heat applications such as cookware and heat exchangers | Aluminum alloyed with manganese | |
| 4000 | Filler material | Aluminum and silicon | Highly weldable | |
| Experience-based Welding | ||||
| 2000 | 2025 | Aluminum and copper | Crack Sensitive | |
| 7000 | 7075 | Marine applications | Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium | Low density and steel-like strength |
Best Practices to Prevent Defects in Aluminum Welding
Aluminum welds are prone to defects after welding. Definitely, you can prevent these defects.
The table below highlights the common defects and how you can prevent them.
| Defect | Type | Best Practice for Prevention |
| Cracking | Hot cracking | Choosing a filler material compatible with the base aluminum. Also, select an ideal welding design |
| Cold cracking | Pre-heating the base material. This will help reduce the cooling speed. | |
| Burn Through or Penetration | When Using MIG welding | Weld at low amperage and use long electrodes. |
| When Using TIG welding | Use a gun capable of pulsing. This will allow intervals for heating and cooling. | |
| Porosity | Bubble-filled welds | Adequately clean the base aluminum before welding. Use the correct shielding gas. |
Properties Making Aluminum Weldable
You can weld aluminum due to the materials:
- High heat conductivity – Allows for quick weld formation.
- Malleability – This reduces the possibility of cracking during welding.
Welding Aluminum To Other Metals
At times, you may find welding aluminum to certain metals to be challenging. A good example is steel- aluminum welding.
This is due to the different physical and metallurgical properties of the two metals.
However, this does not mean you can not weld the two metals. Aluminum is weldable to other metals but will require expertise.
Welding aluminum to other metals is helpful when you need to use only a component of aluminum in a structure made from another metal.
Conclusion
Aluminum welding has its complexities as highlighted in the previous section. However, we trust that this guide has given a passage into the aluminum welding world.
For all your aluminum welding questions or inquiries, KDM is here to help – contact us now.
More Resources:
Sheet Metal Welding – Source: KDMFAB
How to Weld Aluminum – Source: UTI
Top Aluminum Manufacturers – Source: KDMFAB
How to MIG Weld Aluminum – Source: WeldGuru
Aluminum Sheet Metal Fabrication – Source: KDMFAB
Welding Aluminum – Source: WeldGuru
MIG Welding Aluminum – Source: Make Money Welding
How to Weld Aluminum – Source: The Instructables
Weld Aluminum Guide – Source TWI




