In this guide, we are going to compare metal injection molding vs die casting process.
As a result, you will know when to choose the best process for metal part manufacturing process.
Take a look:
Definition: Metal Injection Molding vs Die Casting
Metal injection molding (MIM) transformed metal in powder form to a homogenous mixture.
This material mix refers to feedstock, then subjected to injection molding for desired shape and solidification.
Die casting makes use of molten metal. You will transform the molten metal into useful product using special mold under high pressure. This will help you create desired products.
MIM Manufacturing Process Vs Die Casting Process
There is significant variation between MIM and die casting processes as you will see shortly.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Process
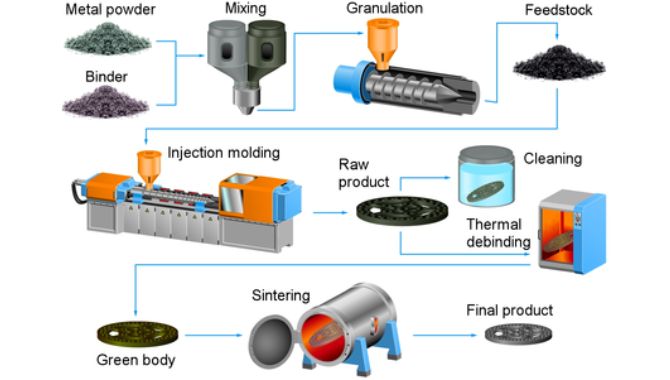
1. Preparing the Feedstock
Preparing feedstock is the first step in MIM. In this step, the metal powder is mixed with the binder. It would help if you kept the metal powder and binder ratio in a ratio of 60:40.
Then it would help if you put the mixture in pelletizing equipment, which first heats the material to melt the binder.
Later even mixing leads to the uniform coating of binder over the powdered metal. After this, cooling leads to the formation of granules or pellets. These pellets then use in the injection molding step.
2. Injection Molding
After preparing the molding equipment, you will add powdered metal alongside the binding solution. It then heats the pellets at high temperatures and injects them into the mold cavity. There the material stays for some time to solidify by successive cooling.
3. DE binding
When the injection molding ends, you will get the final component. Now you need to subject this component to the de-binding. The binding material you used earlier is removed in this step. The solvent extraction method removes the binder. The semi-porous microscopic structure allows the binder to escape through.
4. Sintering
After de-binding, you need to put the component into the sintered furnace. Here the component faces a lot of heat and shrinkage. This process removes any binding material that has been left. After finishing this step, you will obtain the component with tight tolerances/ dimensions as per requirement.
5. Finishing
Finishing, in actuality, is not a step of the Metal Injection Molding. But if needed, you can subject the sintered component to further machining. This may include heating to obtain desired physical properties. Or trimming, polishing, grinding, silk screening, etc., to obtain desired tolerances or dimensions.
Die Casting Process
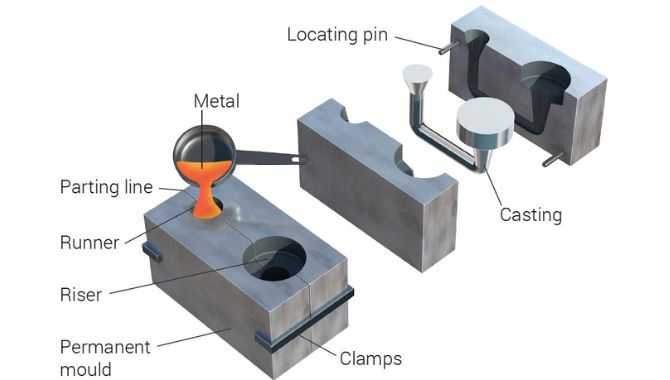
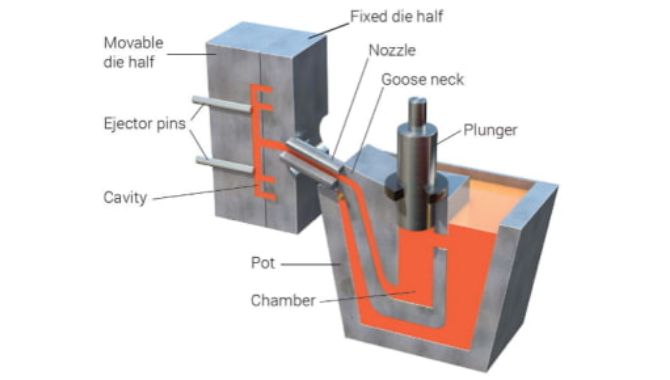
1. Die Preparation
The first step involves die preparation. In this step, you spray with lubricant inside the die and heat it to a suitable temperature. Later you clamp and close the die halves together tightly for further process subjection.
2. Injection
In this step, you need to force the molten metal obtained from the furnace. You do this under high pressure and temperature within the mold. This way, molten material gets evenly distributed throughout the die.
3. Cooling
After putting the molten metal in the cast, you need to leave it for some time to process Cooling and solidification.
4. Ejection
After solidification, open up the die halves and remove the casted component. You can use your hands or even ejector pins to do this.
5. Trimming
In the final step, you perform trimming. During solidification, there are chances that some material solidifies at gates, sprues, runners, and flash. You can use multiple tooling to remove any unwanted particles.
Manufacturing Materials: Metal Injection Molding vs. Die Casting

Best Material for Metal Injection Molding
Please note that manufacturing material decides the end properties of the component. For the processes, you may consider these materials:
MIM Materials:
| Sr. No. | Materials | |||
| Ferrous Alloys | Tungsten Alloys | Hard Materials | Special Materials | |
| 1 | Steel | Tungsten heavy alloy | Cermets | Titanium alloy |
| 2 | Stainless steel | Tungsten copper | Cemented carbides | Cobalt chromium |
| 3 | Iron Nickle magnetic alloy | Molybdenum | ||
| 4 | Invar | Molybdenum copper | ||
| 5 | Kovar | Nickel | ||
| 6 | Nickel Base Superalloy | |||
Material Die Casting
Die casting utilizes non-ferrous alloys principally to manufacture die-casting components. The common materials include:
| Sr. No. | Materials |
| Non-Ferrous Alloys | |
| 1 | Lead |
| 2 | Pewter |
| 3 | Tin Based Alloy |
| 4 | Magnesium |
| 5 | Copper |
| 6 | Aluminum |
| 7 | Zinc |
Metal Injection vs Die Casting – Key Applications

MIM Parts Examples
| Sr. No. | Applications | ||||
| Firearms | Medical Field | Automobile field | Electronics | Aerospace Industry | |
| 1 | Riggers | Joint replacement | Turbocharger | Heat sinks | Flap screws |
| 2 | Magazine catch | Articulation gears | Rocker’s arms | Cold plates | Valve holders |
| 3 | Fire suppression | Devices for drugs | Shift levers | Phone Components | Engine components |
| 4 | safety | Lightening connectors | Rocket burners | ||
| 5 | Fiber Optic Components | ||||
Die Casting Parts Examples
| Sr. No. | Applications | ||
| Lawn/ Garden/ Recreation Industry | Medical Industry | Automotive Industry | |
| 1 | RV Chassis | Computer cover | Gear housing |
| 2 | Steel liner inserts | Hospital equipment controls | Transmission housing |
| 3 | Marine Undercuts | Surgical devices | Retainers |
| 4 | Gear cases | Peristaltic pumps | GPS and Entertainment system housing |
| 5 | Hydrostatic axles | Blood analysis machines | Engine components |
| Power train Systems | |||
Running Costs for Metal Injection Molding VS Die Casting
When comparing the running cost, the die casting is a clear winner compared to the metal injection molding. For operational expenses, die casting is a cheap process.
For die casting, the cost lies in thousands of dollars; for metal injection molding, the cost lies in tens of thousands.
Parameters Influence MIM vs Die Casting
Even before choosing this process, it is important to know factors affecting part quality and cost. Let’s look at some common parameters:
| Sr. No. | Parameters | Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Die casting |
| 1 | Density | 98% | 100% |
| 2 | Mechanical Strength | High | High |
| 3 | Surface Finish | High | Medium |
| 4 | Miniaturization | High | Low |
| 5 | Geometric Complexity | High | Medium |
| 6 | Design Flexibility | High | Medium |
| 7 | Thin Wall Capability | High | Medium |
| 8 | Material Ranges | High | Medium |
| 9 | Product-ability | High | Medium |
| 10 | Post-operation Feasibility | Good | Good |
| 11 | Dimensional Tolerance | High | Medium |
Pros and Cons of MIM and Die Casting
Like any manufacturing process, metal die casting and metal injection molding has its benefits and limitations. Take for example;
Metal Injection Molding Pros
- You can get the final product in accurate dimensions and finish. There is no need to employ further finishing and machining.
- It is a perfect choice for multiple alloys
- You can create any shape, even with complex structure and geometry
- The option exists to make production adjustments in a convenient manner
- It offers zero adverse impact on the tooling. This means you need to spend lower on your tools.
- You can treat the surface of the component any way you like. It offers compatibility with different surface treatments.
Metal Injection Molding Cons
- It costs more in comparison to the die casting
- The die life in this process is very low. It supports shots that range from 150,000 to 300,000.
- There is a possibility of parts shrinking by about 30%
- The initial setup requires substantial expenses
Die Casting Pros
- Help you save more than 30% on expenses in comparison to Metal injection molding
- Die casting allows you to enjoy longer die life with up to 1 million shots
- Die casting is completely automated. You don’t need to spend on labor costs
- Supports a plethora of applications in multiple industries
- The option exists to create complex inserts or fasteners for end products
Die Casting Cons
- You may face porosity in the challenging end product
- The die usually cost more which require subjection to the higher temperature and higher pressure
- The setup cost for die casting is higher
- Not suitable to carry out the production on smaller volume
Feed Wastage: Metal Injection Molding vs. Die Casting
Feed wastage indicates the material that is of no use or refers to scrap. The more waste generated, the lower the efficiency of the process.
In die casting, the scrap or waste generation is higher than the feed waste in metal injection molding. When it comes to material consumption, MIM utilizes low material quantity. The main reason behind less waste generation is the automatic system of feeding. MIM generates less than 5% of waste compared to die casting.
Conclusion
Even as we compare metal injection molding vs die casting, it is quite clear that they play a significant role in metal parts manufacturing.
From above information, it is evident that the cost, manufacturing process, and part quality vary depending on the process.
More Resources:
Die Casting – Source: Wikipedia
Die Casting Process – Source: Dynacast
Metal Die Casting – Source: Custom Part
Metal Injection Molding – Source: Wikipedia
MIM – Source: Custom Part
MIM Process – Source: IQS Directory
Sheet Metal Fabrication – Source: KDM




